Alkynes
- Alkynes have one (or more) carbon to carbon triple bond(s).
- As a result of the triple bond, alkynes have fewer hydrogen atoms than alkanes and even fewer hydrogen atoms than alkenes. Therefore, alkynes are referred to as unsaturated like alkenes.
Structure of Alkynes
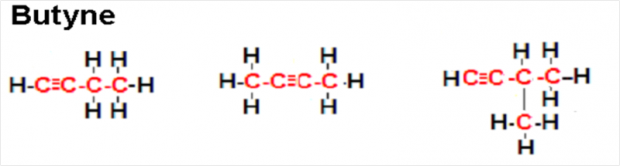
Structural Isomers of Butyne
- Like alkanes and alkenes, alkynes can have straight chains or branched chains.
- In the longer-chained alkynes, there are more locations for the carbon to carbon triple bond. Hence, more structural isomers are possible.
- The first structural isomer of butyne (refer to the picture above) has a straight chain in which the triple bond lies between the first and second carbon atoms.
- The second structural isomer of butyne also has a straight chain; however, in this isomer the triple bond lies between the second and third carbon atoms.
- The third structural isomer of butyne displayed above has a branched chain. Note: The triple bond can occur in one of the branches but branches cannot be attached to any carbon in the triple bond.
