Alkenes
- Alkenes have one carbon to carbon double bond (C=C).
- Alkenes are considered to be unsaturated hydrocarbons, since they have fewer hydrogen atoms than alkanes as a result of the double bond.
- Like alkanes, alkenes can have straight chains or branched chains.
- In the longer-chained alkenes, there are more locations for the carbon to carbon double bond (C=C). Hence, more structural isomers are possible.
Structure of Alkenes
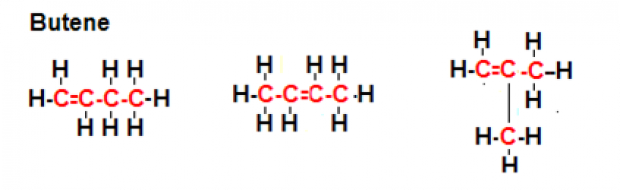
Structural Isomers of Butene
- The first structural isomer of butene (refer to the picture at the left) has a straight chain in which the double bond lies between the first and second carbon atoms.
- The second structural isomer of butene also has a straight chain; in this isomer, however, the double bond lies between the second and third carbon atoms.
- The third isomer of butene, unlike the previous structural isomers, has a branched chain, since a methyl group is attached to the second carbon atom.
